Abstract
Tactile Walking Surface Indicators (TWSIs) are safety-critical landmarks that blind and low-vision (BLV) pedestrians use to locate crossings and hazard zones. From our observation sessions with BLV guide dog handlers, trainers, and an O&M specialist, we confirmed the critical importance of reliable and accurate TWSI segmentation for navigation assistance of BLV individuals.
Achieving such reliability requires large-scale annotated data. However, TWSIs are severely underrepresented in existing urban perception datasets, and even existing dedicated paving datasets are limited: they lack robot-relevant viewpoints (e.g., egocentric or top-down) and are geographically biased toward East Asian directional bars.
We introduce GuideTWSI, the largest and most diverse TWSI dataset, which combines a photorealistic synthetic dataset, carefully curated open-source tactile data, and quadruped real-world data collected and annotated by the authors. Notably, we developed an Unreal Engine-based synthetic data generation pipeline to obtain segmented, labeled data across diverse materials, lighting conditions, weather, and robot-relevant viewpoints.
Extensive evaluations show that synthetic augmentation improves truncated dome segmentation across diverse state-of-the-art models, with gains of up to +29 mIoU points, and enhances cross-domain robustness. Moreover, real-robot experiments demonstrate accurate stoppings at truncated domes, with high repeatability and stop success rates (96.15%).
Key Contributions
- Photorealistic Synthetic Data Pipeline: Unreal Engine 4-based pipeline specifically designed for blind navigation, simulating multiple truncated dome textures under diverse viewpoints and lighting conditions, generating over 15K samples.
- Large-Scale GuideTWSI Dataset: Comprising (i) meticulously curated open-source annotations (RBar-22K), (ii) our synthetic data (SDome-15K), and (iii) real-world robot-collected data (RDome-2K), all released with code and pretrained model weights.
- Extensive Evaluations: State-of-the-art segmentation models showing up to +29 mIoU improvement with synthetic augmentation, demonstrating robustness across domains.
- Real-World Robot Deployment: Guide dog robot stopping at truncated domes with a success rate over 96% across diverse, previously unseen real-world environments.
Photorealistic Synthetic Tactile Paving Dataset Generation
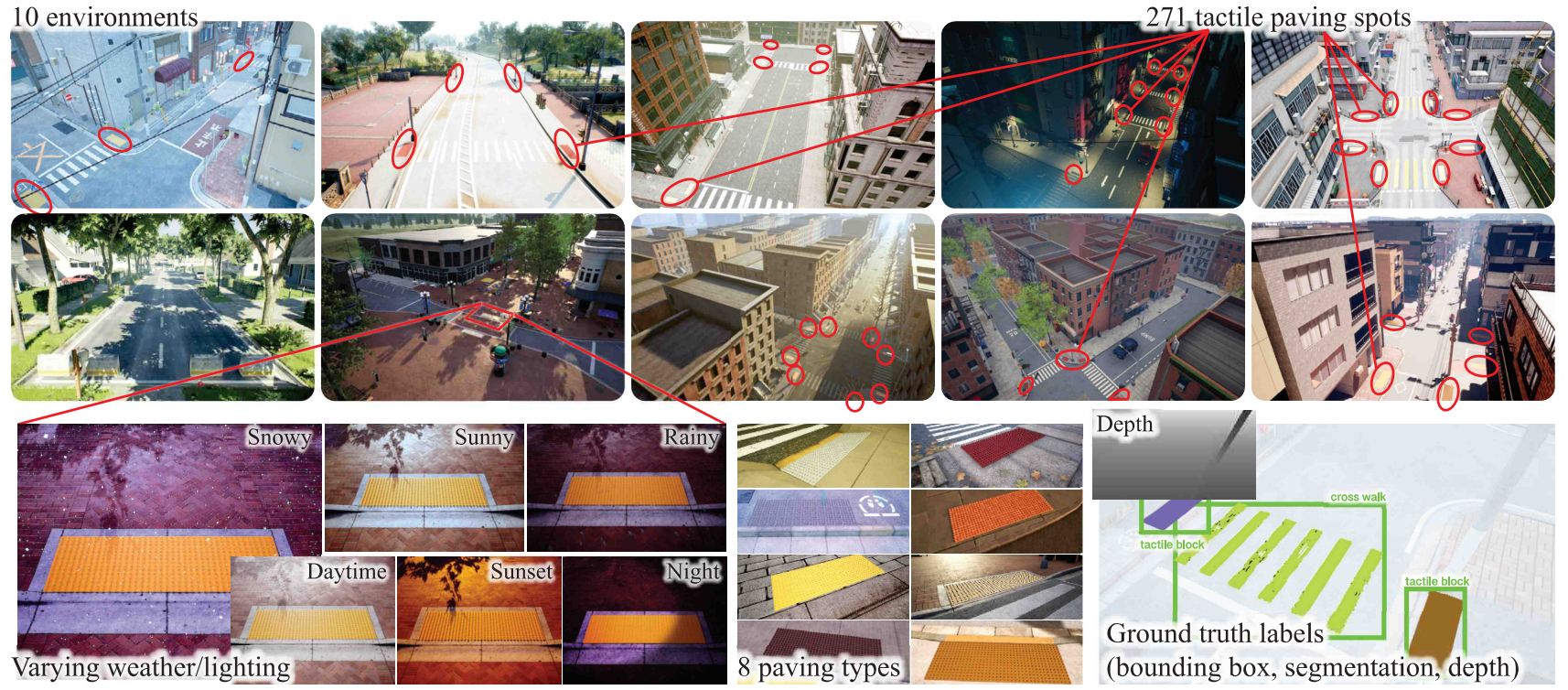
Our synthetic data generation pipeline uses various sidewalk environments in Unreal Engine 4 with varying viewpoints, lighting, and weather conditions to simulate real-world variability. We use AirSim for automatic annotation of depth, instance masks, and bounding boxes.
Dataset Components:
| Dataset | Scale | Type | Geography | Modalities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBar-22K (compiled) | ~22K | Real/bars | Mostly Asia | RGB, Seg. |
| RDome-2K (ours) | 2.4K+ | Real/domes | United States | RGB, Seg. |
| SDome-15K (ours) | 15K+ | Synthetic/domes | Simulated | RGB+D, BBx, Seg. |
Real Robot Data Collection and Hardware Experiment
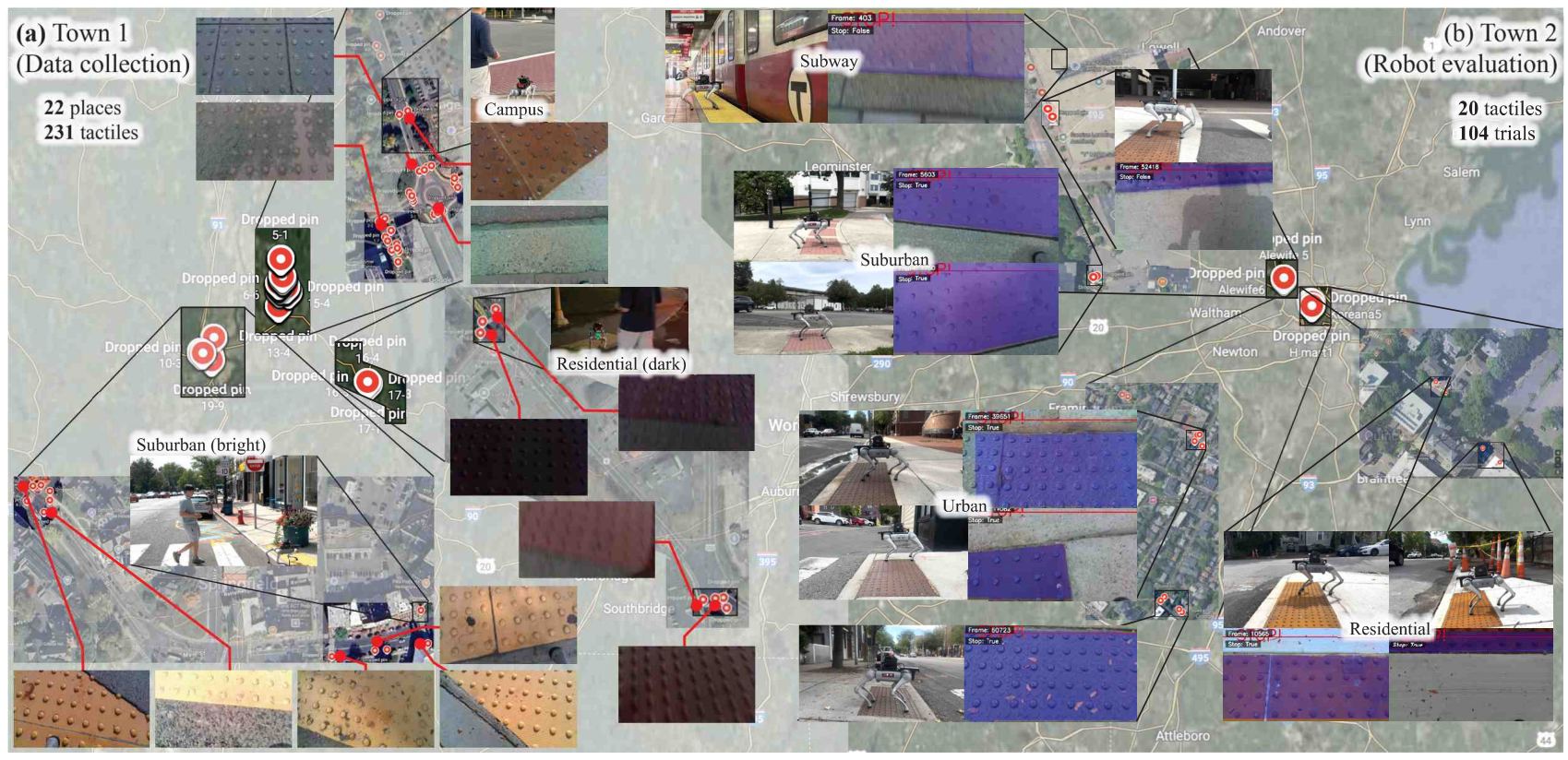
We integrated our fine-tuned segmentation model into a fully untethered guide dog robot platform. The system is built upon the Unitree Go2 quadruped robot equipped with a RealSense D435 camera positioned with a downward tilt for truncated dome segmentation.
The model was converted to a TensorRT-optimized engine, achieving up to 43 FPS inference on an NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin. Our system employs segmentation-based closest-point detection strategy, identifying the lowest truncated dome-pixel in the image frame as the point closest to the robot body.
Experimental Results
Impact of Synthetic Data Augmentation on Truncated Dome Segmentation
| Method | Real Data Only | Real + Synthetic | Delta mIoU | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP50-95 | mIoU | mAP50-95 | mIoU | ||
| YOLOv11-seg-N | 0.5934 | 0.6161 | 0.7288 | 0.7308 | +0.1147 |
| YOLOv11-seg-X | 0.7362 | 0.7389 | 0.8188 | 0.7887 | +0.0498 |
| Mask2Former | 0.4798 | 0.5777 | 0.7829 | 0.8375 | +0.2598 |
| SAM2.1+UNet | 0.3475 | 0.4789 | 0.5627 | 0.6883 | +0.2094 |
| DINOv3+RegCls | 0.6176 | 0.7322 | 0.6933 | 0.7926 | +0.0604 |
| DINOv3+EoMT | 0.4828 | 0.5804 | 0.8492 | 0.8756 | +0.2952 |
Robot Stopping Performance
| Environment | N (locations) | Mean Distance (cm) | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | 6 | 35.2 +/- 9.2 | 29/30 |
| Urban2 | 5 | 47.1 +/- 15.6 | 25/25 |
| Suburban | 6 | 38.2 +/- 14.4 | 32/34 |
| Residential | 3 | 34.6 +/- 14.2 | 14/15 |
| Overall | 20 | 39.0 +/- 14.3 | 100/104 (96.15%) |
Qualitative Results
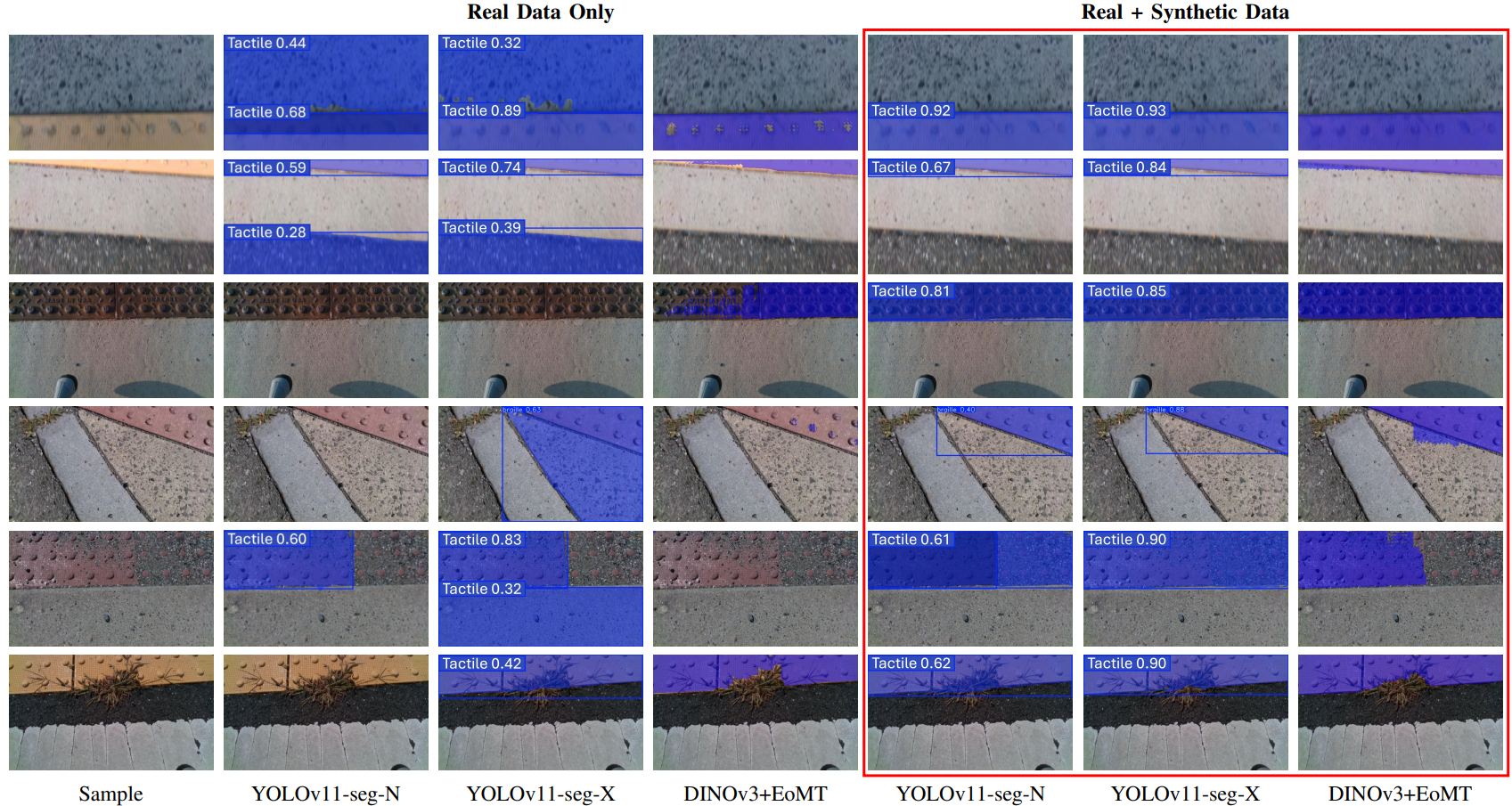
Qualitative comparison of segmentation models trained on real data only vs. real + synthetic data. Models trained with synthetic data produce sharper boundaries and fewer missed detections, especially under challenging textures and lighting.